Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent






Injection parts usually refer to their toughness and rigidity. What is the difference?
Toughness refers to the ability of a material to absorb plastic deformation work and fracture work before fracture, which characterizes the performance of a material against crack propagation. It can usually be measured by the area under the engineering stress-strain curve. The larger the area, the higher the toughness and the better the fracture resistance. Strong, only when the abscissa and ordinate of the stress-strain curve (ie strength and strain) are relatively large, the toughness is high. If the strength is too low, even if the ductility is large, the toughness will not be too high. So toughness is a comprehensive index of strength and plasticity.
That is to say, toughness refers to the amount of energy absorbed by the material before failure and the ability to plastically deform, as opposed to brittleness. Therefore, the larger the deformation and the larger the fracture work on the tensile curve, the better the toughness. Impact strength can usually be used to evaluate, because impact strength is generally expressed in terms of work at break.
Plasticity is a material property that causes permanent deformation of a material under a given load. For most engineering materials, when the stress is lower than the proportional limit, the stress-strain relationship is linear. Additionally, most materials behave elastically when their stress is below the yield point, that is, when the load is removed, the strain also completely disappears. Plasticity is usually measured by elongation and reduction of area.
Tensile strength: It seems to be related to the bond energy, but for polymers, the tensile failure in most cases is not the destruction of the bond, but the change of the slippage and aggregation state between the molecular chains, so it is mainly related to the molecular The interfacial force is related to the degree of crystallinity.
Rigidity is usually measured by flexural strength. Polymers are usually evaluated from three aspects: strength, hardness, softness, and brittleness.

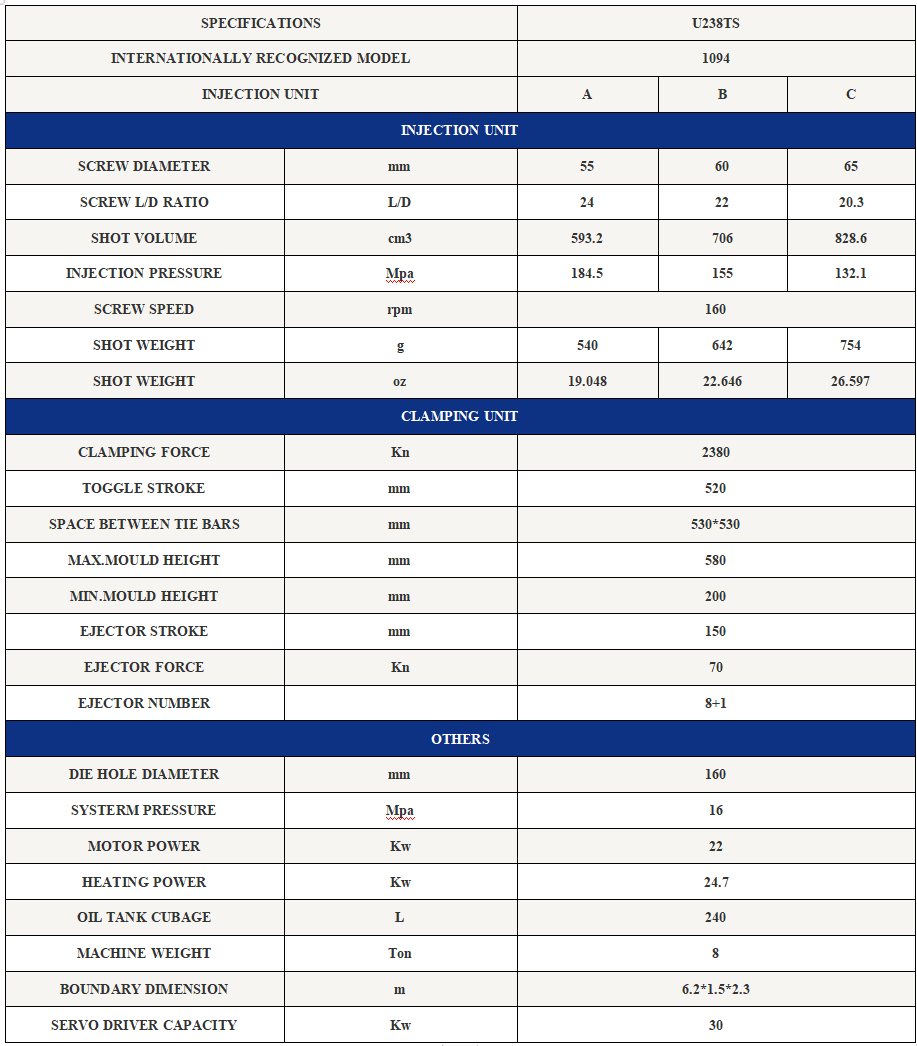
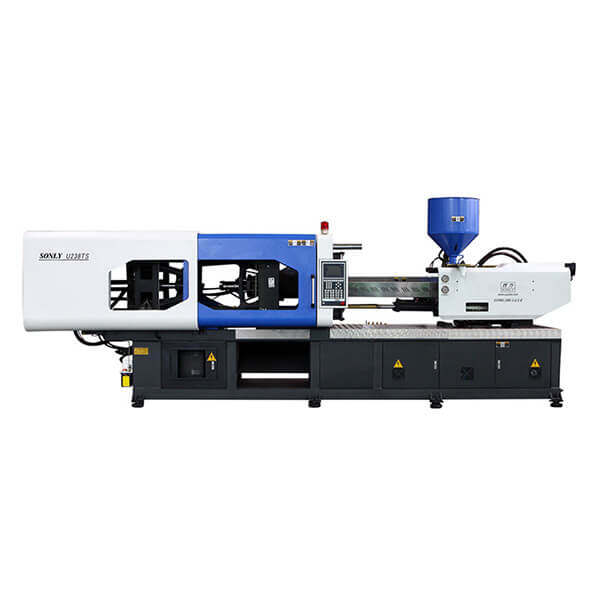
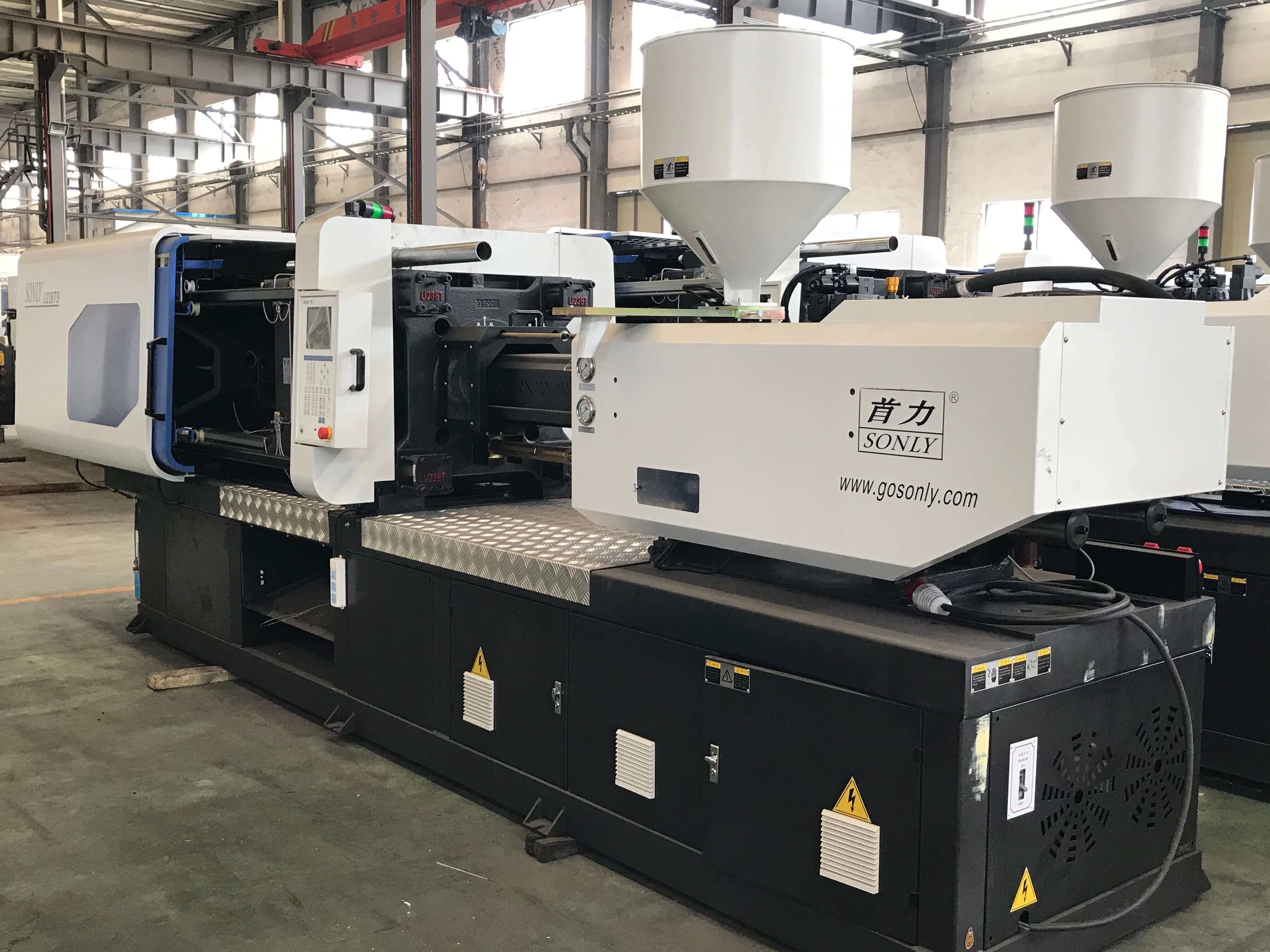
Main Features:
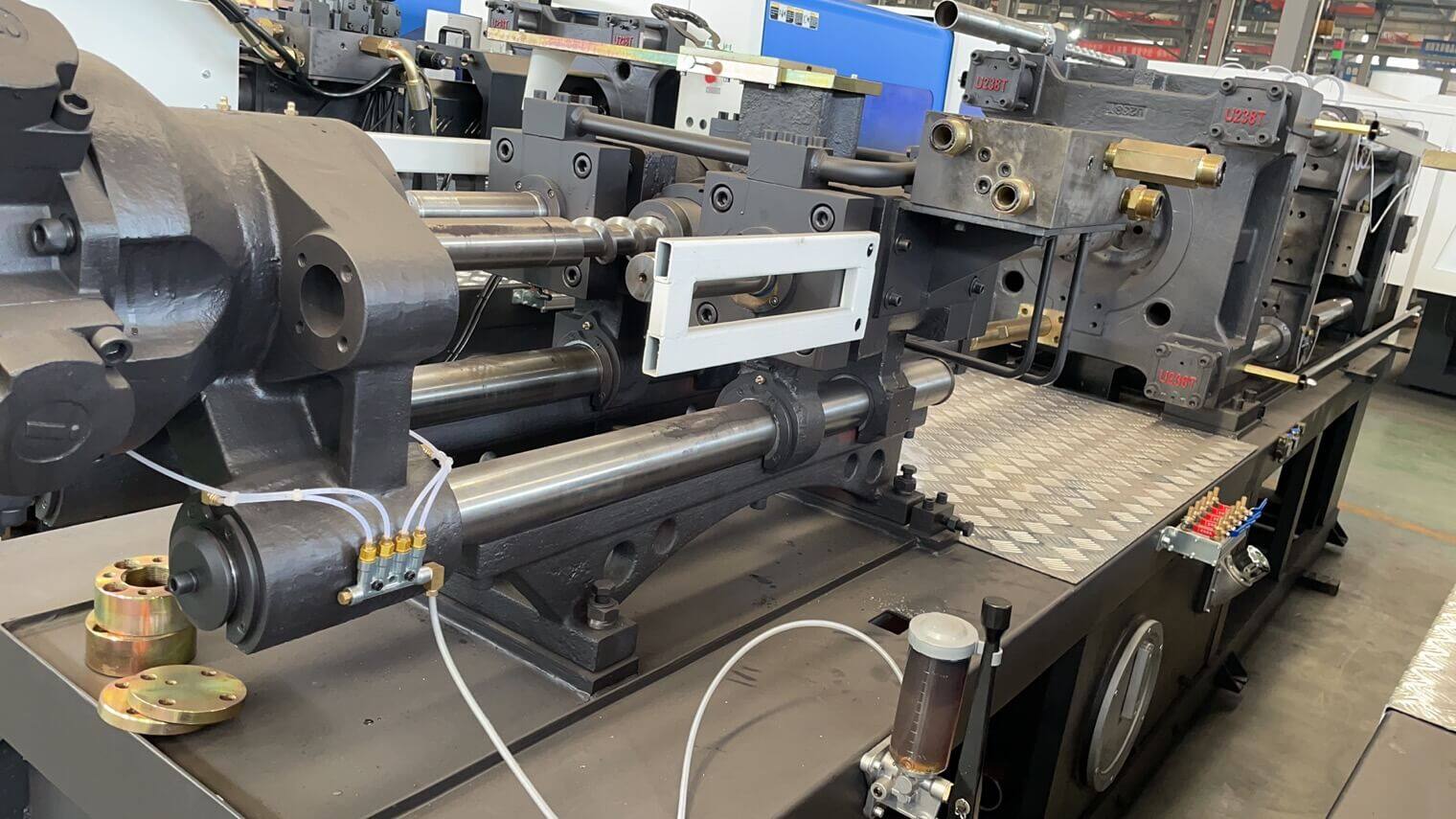
One.The Lock Section
1.Arch template, effectively protects the mould, especially suitable for big template with small mold.
2.The electric ruler is installed on the crosshead, the position is more precise.
3.The front connecting rod uses connected structure, increases the rod strength, and easy for assembly
4.The connected tail-board stills itself with big lock shaft, improves tail-board strength, and ensures zero abrasion of the tail-board, easy for maintenance.
5.Connected movable plate, improves its rigidity and reduces deformation
6.Connected thrust bearing, improves its strength and stills itself with small lock shaft, ensures zero abrasion.
7.Arch template fully complies with mechanical property, largely improves template strength.
8.More reasonable toggle design, speeds and stabilizes mold opening and closing.
9.Adjustable movable plate mounting plate, makes the installation easier.
10.Mixed design of T-shape groove and die hole, increases universality of the mold.
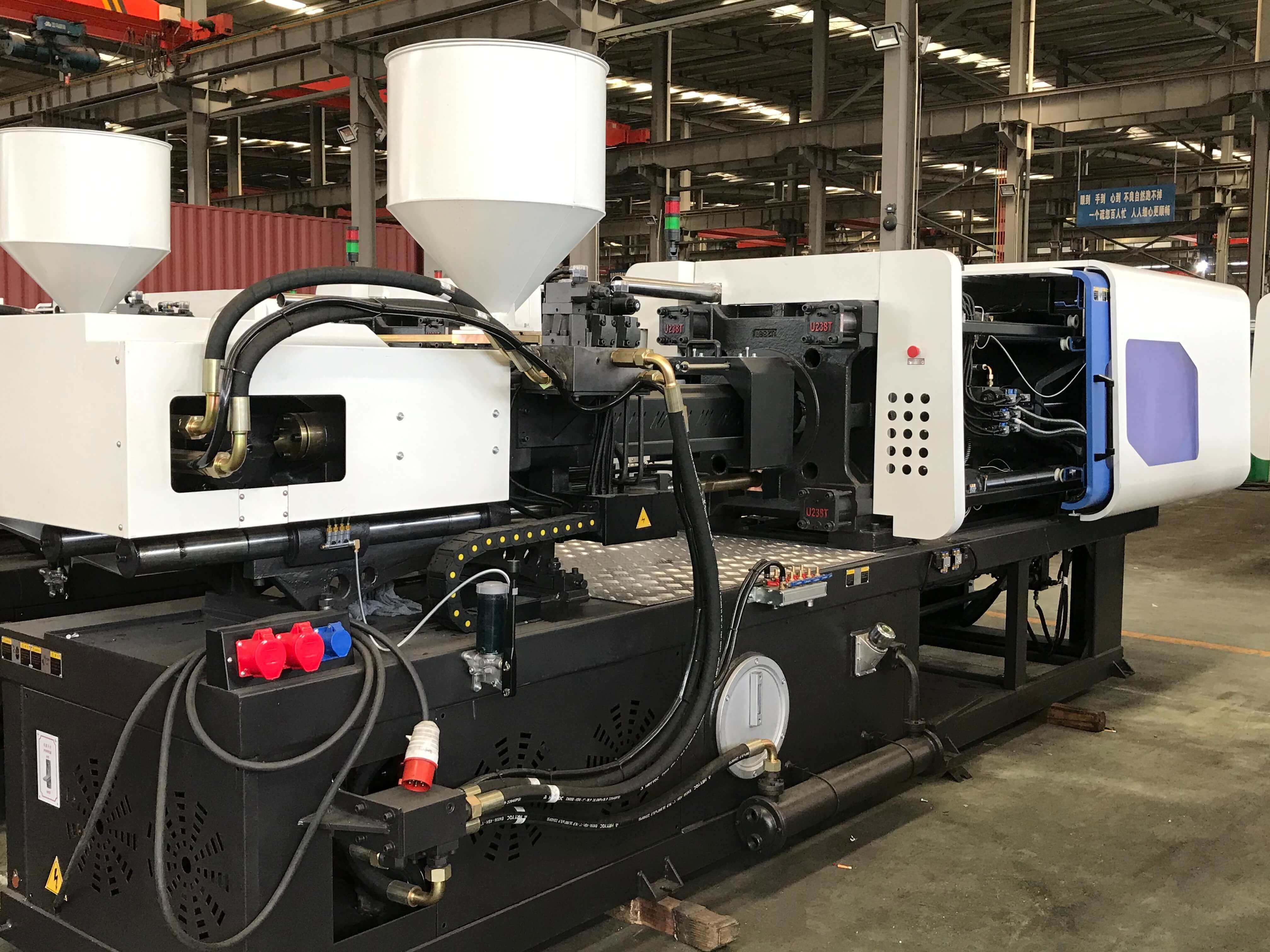
Two.The Injection Section.
1.Bridge type support, improves injection smoothness.
2.Longer length-diameter ratio screw design, improves plasticizing effect.
3.Double seal structure, ensures no oil leakage.
4.Withhold type press plate, easy for debugging and assembly.
5.Bijection structure, improves stability.



